It’s been a big week for reports that will be useful to those working to enable a broad range of off-grid energy solutions for the 1.2 billion people currently lacking access to modern energy.
First, today marks the release of the much-anticipated Off-Grid Solar Market Trends Report 2016, published by Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) and the World Bank Group’s Lighting Global program, in cooperation with the Global Off-Grid Lighting Association (GOGLA). The report addresses trends in markets for off-grid solar products and services, noting that annual investments into the sector have risen 15-fold from 2012 to $276 million in 2015 alone. To put this rapid investment spike in context: the total investment in the sector to date is $511 million.
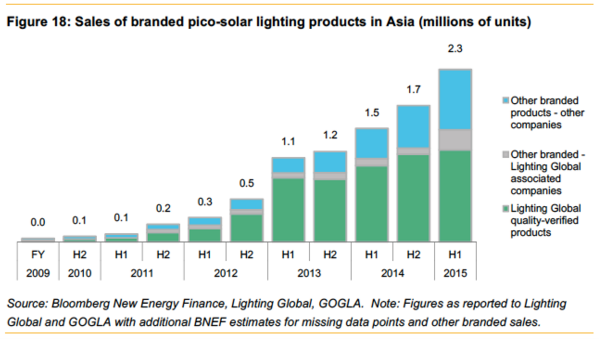
This report also includes information on sales of off-grid products, including a breakdown of sales by product feature and a breakdown of pico-solar lighting product sales in Asia and Africa. Sales of pico-solar lighting products in Asia are depicted in Figure 18 below.
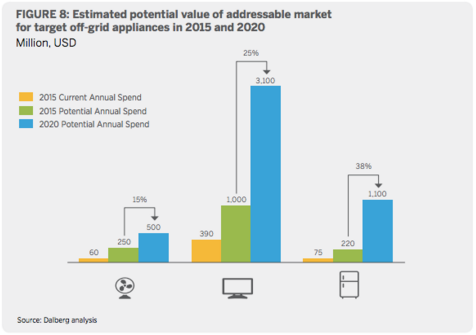
And earlier this week, Global LEAP, a part of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Clean Energy Ministerial Initiative, released The State of the Global Off-Grid Appliance Market, describing the state of the market for highly energy-efficient appliances, including fans, televisions, and appliances. The efficiency of these appliances and LED lights has been transformative, allowing off-grid solar to improve the lives of 89 million people in Africa and Asia. The report estimates that by 2020, consumer spending on off-grid fans, televisions, and refrigerators could reach $4.7 billion per year (up 800 percent from $525 million in 2015). This is captured in Figure 8 below, which is broken down by appliance.
The market trends report includes a broader range of technologies than in its 2010 and 2012 reports and also pays specific attention to Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) models, which provide consumers with more flexible payment options. In 2014 and 2015, PAYG companies received 87 percent of direct investments into off-grid solar companies. These companies will likely continue to attract the most attention. The diagram below, from the BNEF, Lighting Global, and GOGLA report, shows a sample of Pay-As-You-Go players along the value chain, including major impact and strategic investors.

While things might be going well for the sector as a whole, challenges certainly exist. For example, the report from BNEF, Lighting Global, and GOGLA notes the proliferation of cheap, generic off-grid products. This threatens market spoilage with unpredictable quality and impacts the sales of quality-assured companies.
Additionally, financing remains a bottleneck, in spite of the huge rise in investments mentioned above. Along with private investors, the U.S. government and multilateral development banks can play a role in alleviating some of these financing challenges through investments and assuming some investment risk through loan guarantees.